Osteoarthritis is a chronic disorder manifested by persistent pain in the joints caused by an abnormal wear of the cartilage and the entire joint. It is the form of arthritis the most common. The most commonly affected joints are the knee, hip, and those of the spine. However, other joints, such as shoulder, ankle, and wrist, can also be achieved. Osteoarthritis of the fingers (digital osteoarthritis) is also very common, especially in women.
Causes
The causes of osteoarthritis are multiple. Mechanical factors are prominent, associated with genetic factors, a process of inflammation, etc. Osteoarthritis is a disease resulting in abnormal cartilage degeneration. Indeed Repetitive movements and repetitive strain injury to a joint, however, Excess weight and lack of physical activity are two other important factors.
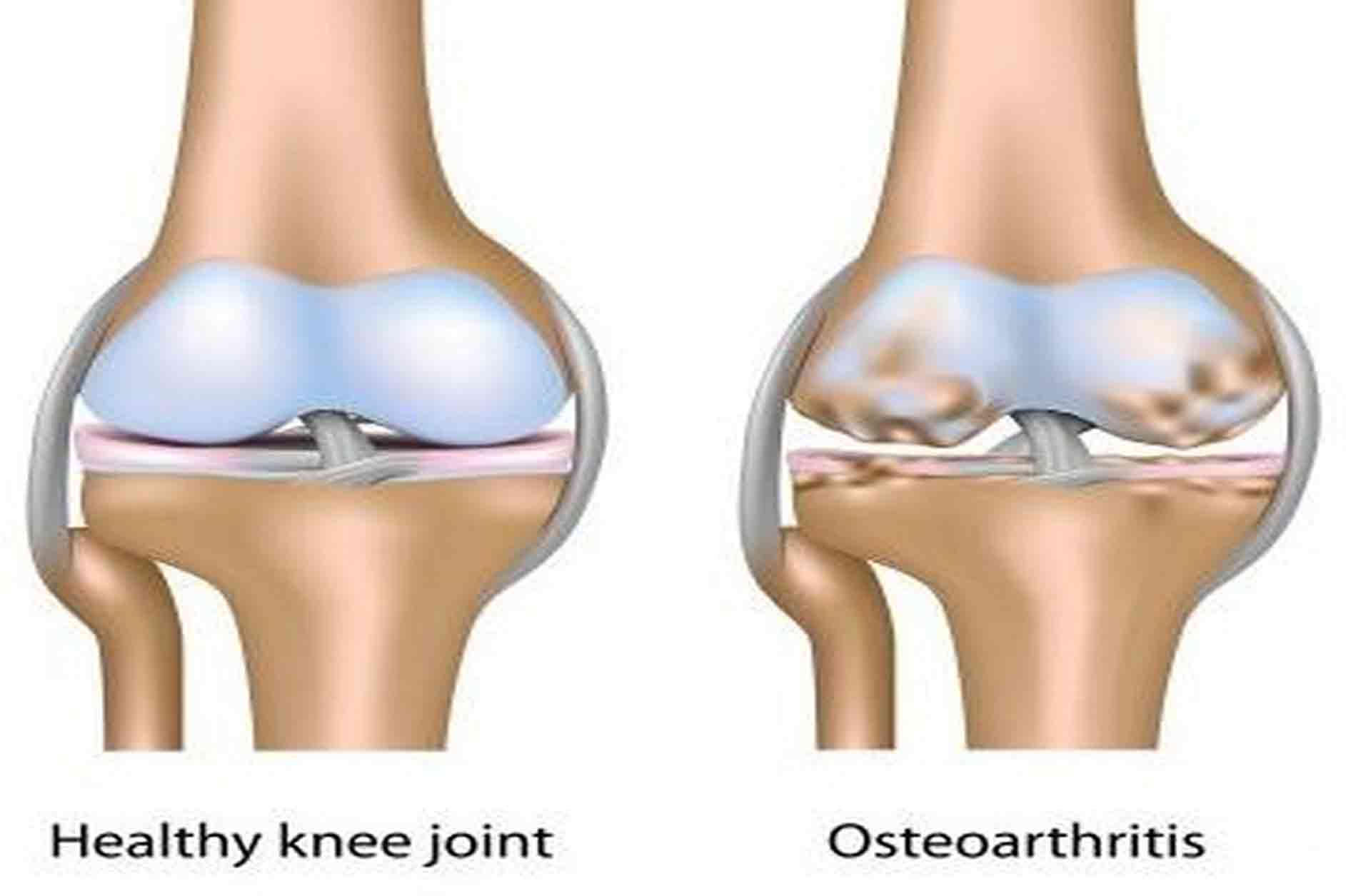
Types of arthritis
- Primary osteoarthritis: When the affected person from osteoarthritis has no obvious predisposition, osteoarthritis of “primary” one qualifies.
- Secondary osteoarthritis: Diseases of the joints, such as inflammatory diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, gout, lupus, etc.) and metabolic disorders (diabetes, hemochromatosis), predispose to osteoarthritis. It is the same injuries and surgeries as a joint. When there is a predisposition by either of these situations, it is secondary osteoarthritis.
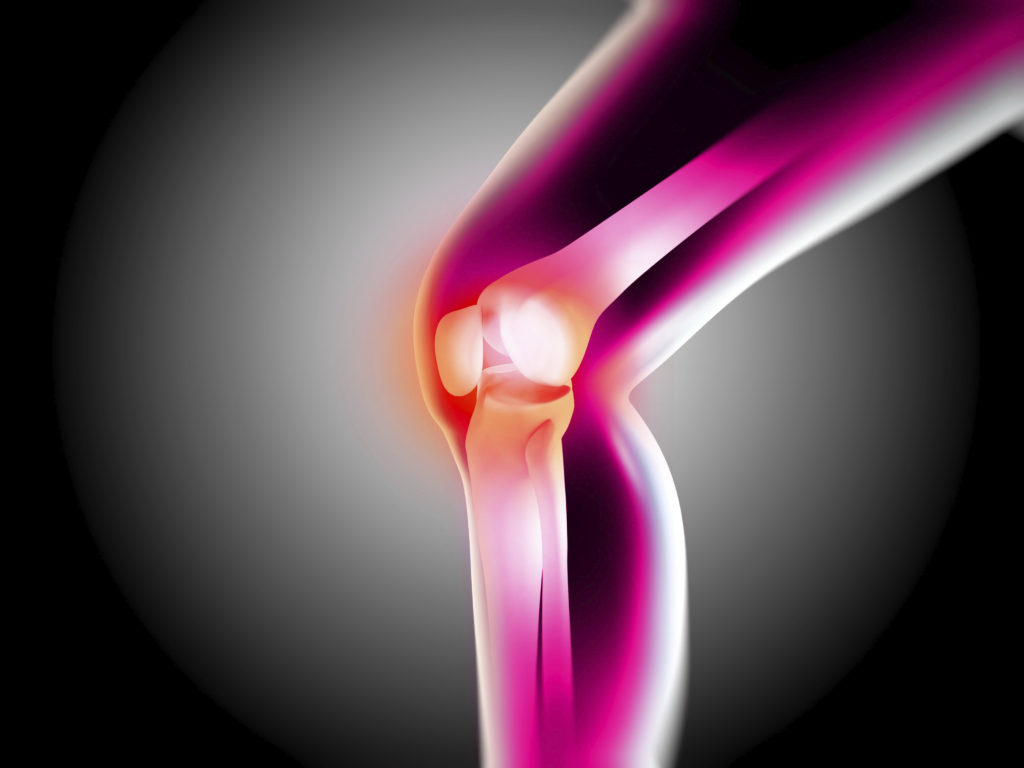
The symptoms of osteoarthritis (OA)
Osteoarthritis reaches each individual differently. The affected joints and intensity of pain vary from person to person:
- Pain in the affected joint mainly when activated (e.g., knee pain down the stairs)
- The sensitivity of the joint when applying slight pressure
- Stiffness of the joints, especially on waking or after a period of immobility. Morning stiffness lasts less than 30 minutes
- A gradual loss of flexibility in the joint
- A feeling of discomfort in the joint as a result of temperature changes
- The “creaking”, especially in cases of knee osteoarthritis
- The gradual appearance of small bony growths (osteophytes) at the joint
- More rarely, inflammation (redness, pain, and swelling of the joint)
If you are worried about a diagnosis of osteoarthritis, consider these major contributing factors. Improving one of these areas could help you reduce your risk of osteoarthritis.
1. Joint injuries
The clinics report that an injury like a broken wrist, ankle, or knee during a fall or a sports activity could increase your risk of osteoarthritis. The reason? An injury to the joint or cartilage makes this area vulnerable to degenerative problems such as osteoarthritis.
2. Type 2 diabetes
A European study in the Diabetes Care journal of the American Diabetes Association found that people who type2 diabetes have a high probability of developing severe osteoarthritis. The study followed for 927 men and women with type2 diabetes and found that participants were more likely to receive joint replacements of the hip or knee than non-diabetics; the hip and knee are the main treatment for severe osteoarthritis.
3. Too many pounds (or kilos)
Wisdom is not the only thing that increases with age. It’s the same for your waistline. Carrying extra weight adds a constant pressure on your joints, causing cartilage degradation. This is especially true for bearing joints: the knees and hips. If you are overweight, lose those extra kilos (or pounds) is one of the most effective treatments against osteoarthritis. A study that followed women of different weights over 36 years found that heavier women (those in the top 20% by weight) were more than three times more likely than women in the bottom 20% of developing severe knee osteoarthritis. This study was the first to show that Osteo-arthritis (OA) can be prevented.

4. Physical exertion at work
Some jobs increase the risk of people developing osteoarthritis. For example, knee osteoarthritis is common among miners, dockers, who must remain in a squatting position for many years, and those who have to constantly bend the knees or lift heavy objects. People in these occupations the risk of developing osteoarthritis of the knee.

5. The genetic factor
Genetics may play a role; if one of your parents is osteoarthritis, you could be affected too. Indeed, at least 50% of osteoarthritis of the hands and hips is due to genetics.
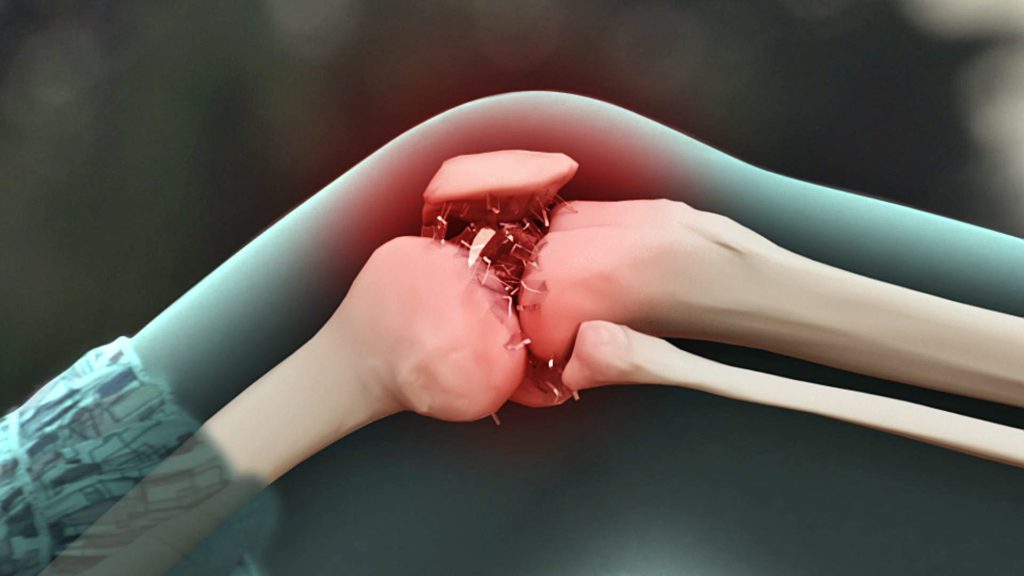
Treatment
One of the easiest ways to help your joints is to take supplements for joint health. drugs contain natural eggshell membrane (NEM), a compound that includes glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, hyaloronique acid, protein, and amino acids, either the main ingredients to fight against the markers of inflammation that degrade collagen. According to Arthritis Research UK, the collagen that built the articular cartilage. More cartilage means more protection between your joints and less pain.
Non-drug treatments
The latest international recommendations said that the importance of non-pharmacological measures to treat osteoarthritis, especially when it affects the knee or hip.
- Regular physical exercise, 15 to 30 minutes at least 3 times a week: walking, swimming, aerobics, adapted strength training, etc. The intensity of the exercises can be adapted to variations in the intensity of pain.
- Weight loss in obese or overweight: lose 5% to 10% of its weight sometimes helps eliminate pain in osteoarthritis of the knee, easing the load on the joint.
- Physiotherapy if necessary
- Adapting the work environment if the job because of joint trauma is causing osteoarthritis.
When they are not enough, these can be supplemented by taking drugs to relieve pain. In more severe cases, the doctor may propose surgery.



