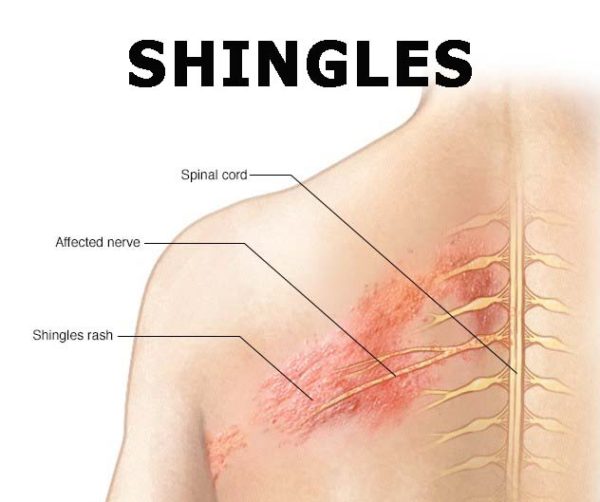
Shingles Viral Infection is manifested by painful rashes along a nerve or nerve ganglion. These eruptions occur as a result of the reactivation of the virus that causes varicella, varicella zoster virus (VZV). Shingles usually affect the chest or face, but all parts of the body affected. Sometimes the pain caused by shingles persists for months or even years after the healing of the rash: this pain called neuralgia or post-zoster pain.
Shingles Viral Infection Causes
- As a result of chickenpox, almost all viruses destroyed except a few. They remain dormant in the nervous ganglia for several years.
- With age or because of a disease, the immune system can lose its ability to control the virus, which can reactivate itself. An inflammatory reaction is then established in the ganglia and nerves, causing the appearance of vesicles arranged in clusters on the skin.
Shingles Viral Infection
It is possible that already infected adults who have been in contact with children with chickenpox benefit from increased protection against shingles. Scientists believe that second exposure to the virus stimulates the immune system and thus helps to keep the virus in a dormant state.
Who Is Affected?
- About 90% of adults worldwide have had chicken pox. They are therefore carriers of the varicella zoster virus.
- About 20% of them are affected by shingles during their lifetime.
Shingles Evolution
In the absence of treatment, the lesions of shingles last on average 3 weeks. Most of the time, a single shingle crisis occurs. However, the virus may reactivate several times. This is what happens in the case of about 1% of the people affected.
Shingles Complications
- The pain sometimes persists after healing of the cutaneous lesions: it is post-herpes neuralgia (or post-zoster neuralgia). This pain compared to that of sciatica. People who suffer from it say they feel genuine “electric shocks”.
- The heat, the cold, the simple friction of a garment on the skin, or the breath of the wind can become unbearable. The pain can last for weeks or months. Sometimes it never stops.
- Every effort made to avoid this situation, which can become a major source of physical and psychological distress. Neuralgic pains, persistent, intense, and difficult to treat effectively.
- Taking antiviral drugs at the onset of shingles would help prevent them.
- The risk of post-herpetic neuralgia increases with age. Thus, according to a study in Iceland of 421 people, 9% of people aged 60 and over experienced pain 3 months after a first shingles attack, compared to 18% of people aged 70 and over.
- Post-shingles neuralgia caused by the damage of nerve fibers, which send confusing messages of pain to the brain.
- Other types of complications may occur, but they are rare: ocular problems (including blindness), facial paralysis, non-bacterial meningitis, or encephalitis.
Shingles Contagion
Shingles are not transmitted from person to person. However, the fluid inside the red vesicles that form during a shingles crisis has several particles of the varicella virus. This fluid is therefore very contagious: a person who touches it can catch chicken pox if it has never had it. To enter the body, the virus must come into contact with a mucous membrane. It can infect someone who rubs their eyes, mouth, or nose, such as, with a contaminated hand.
Washing hands helps prevent the transmission of the virus. It is also advisable to avoid physical contact when the liquid flows from the vesicles. People who have not had chicken pox and whose infection may have serious consequences should exercise extra caution: such as, pregnant women (infection dangerous to the fetus), People whose immune system, weakened and newborns.

Shingles Symptoms
- The person with shingles experiences a burning sensation, tingling, or increased sensitivity on an area of the skin along with a nerve, usually on only one side of the body.
- If it occurs on the thorax, shingles can create a more or less horizontal pattern that evokes the shape of a Hemi-belt (in Latin, shingles means belt).
- From 1 to 3 days later, a diffuse redness appears in this region of the skin.
- Then, several red vesicles filled with liquid and resembling the pimples of chickenpox erupted. They cause itching, dry out in 7 to 10 days, and disappear after 2 to 3 weeks, sometimes a little longer.
- 60% to 90% of people with shingles experience acute local pain, varying in duration and intensity. It may resemble that of a burn or electric shock, or acute stitches. Sometimes it is so strong that it can be confused with a heart attack, appendicitis, or sciatica.
- Some people have fever and headaches.

People at Risk
Shingles are more common in people aged 60 years and older because immunity weakens with age and the virus can multiply more easily. Various treatments and health problems increase the risk of shingles by weakening immunity (cancer, diabetes, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, etc.). However, this type of risk factor is present in only 4% of the people affected.
Risk factors
No risk factors are officially recognized. The researchers question whether there is a possible link between the onset of shingles and the fact of experiencing chronic stress. Studies carried out to date lead to contradictory results: some suggest a link, and others, not. A study in North Carolina suggests that exposure to chemicals increases the risk of shingles. The study included 900 participants between the ages of 18 and 40 who live within 2.5 miles of a pesticide or other chemical landfill site. These participants suffered from zoster seizures twice as much as the 742 respondents living at a greater distance from the site in the surrounding communities. According to the authors of the study, exposure to certain chemicals would weaken immune defenses.
Measures to prevent the onset of shingles
- The best way to prevent it is not to get chicken pox. However, this is not simple, as this virus spreads easily in infants.
- Varicella vaccination may provide protection against shingles. However, it will take several more years to verify this hypothesis, given that this vaccine is only available since 1998 in Canada and 2004 in France. Note that the varicella vaccine is also intended for adults who have never had chicken pox.
- Strengthen your immune system: To prevent the virus from becoming active, it is best to strengthen its immune system through a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and adequate rest periods.
- Zostavax® is a new vaccine that helps prevent shingles. It is intended for people aged 60 years and over (65 years in France) who have already had chicken pox. It is obtained by prescription and includes certain contraindications. This vaccine is different from that used to protect against varicella.
Measures to prevent post-herpetic neuralgia
- It is important to consult a doctor as soon as the symptoms of shingles appear. It will prescribe antiviral treatments. When these are taken early, they probably help to limit the onset of post-herpes neuralgia.
- If neuralgia occurs, early antivirals may shorten the duration.
- To avoid complications in the eyes, it is also important to see an ophthalmologist as soon as the shingles touch the upper part of the face.