A cerebrovascular accident (CVA), or stroke, is an abnormal flow of the blood that affects a region more or less of the brain. It occurs as a result of a blocked or damaged blood vessel and leads to the death of nerve cells that are deprived of oxygen and nutrients essential to their functions. In most people, there is no precursor to an attack. However, several risk factors were monitored. Strokes have very different consequences. More than half of the people affected negatively. About 10% of individuals are entirely cured. The risk depends on the region of the brain damage and the functions it controls. The more oxygen-starved part, the greater the effects are likely to be necessary. Following a stroke, some people have difficulty speaking or writing, and he has a problem in memory. They may also be achieved a more or less substantial paralysis of the body.
Stroke types
Ischemic stroke
In eight out of ten cases, strokes are ischemic strokes: the interruption of blood flow is due to a clot (coagulated blood) that blocks an artery to the brain. The leading cause is atherosclerosis; it is an accumulation of cholesterol deposits on the artery walls. These deposits progressively harden and form atherosclerotic plaques that narrow the arteries and promotes clot formation. In some cases, a plate fragment can also break off and obstruct an artery within the brain. Sometimes, the origin of the stroke is the formation of a blood clot away from the brain, for example, in the heart. The blood then carries this clot to the brain.
Hemorrhagic strokes
They are less common (20% of cases). Stopping the flow of blood is due to the rupture of an artery of the brain.
The leading cause of hemorrhagic stroke is high blood pressure. In some cases, the rupture can occur on a pre-existing condition of the artery aneurysm or arteriovenous malformation.
Cerebral thrombosis
It represents from 40% to 50% of cases. It occurs when a blood clot forms in a cerebral artery, a lipid plaque (atherosclerosis).

Stroke: medical emergency
When nerve cells are deprived of oxygen, if only for a few minutes, then die. Also, the time between stroke and medical care is short; the risk of a severe sequel is shrinking. Whatever the damage caused by oxygen deprivation, the brain has some adaptability. Healthy nerve cells sometimes manage to take over the dead cells if they are stimulated by various exercises.

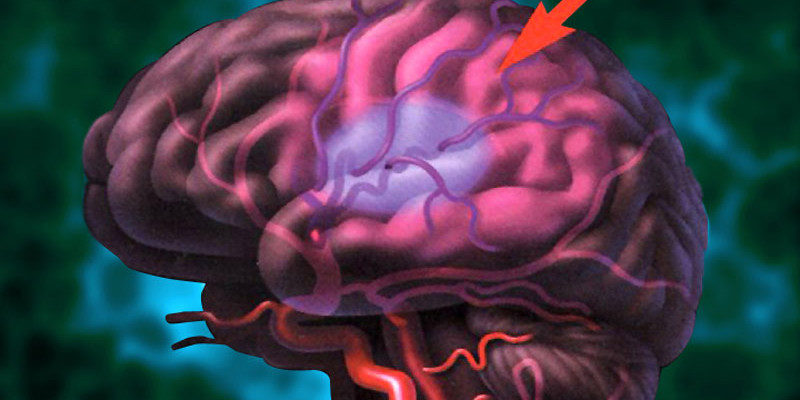
Stroke causes
Atherosclerosis, that is to say, the formation of lipid plaques on the walls of blood vessels is one of the major causes of stroke. Hypertension is a significant risk factor. Over time, the abnormal pressure exerted by the blood on the wall of blood vessels can cause them to break. The presence of an aneurysm can facilitate the rupture of an artery in the brain. The aneurysm is a swelling of a small section of an artery due to weakness of the wall. It is not always possible to determine the exact cause of stroke. It is essential, however, that doctors seek it by performing various tests to reduce the risk of recurrence.
What are the symptoms of the stroke?
In general, there are no or few signs that herald the onset of a stroke. Symptoms appear suddenly and depend on the area of the brain damage:
- Numbness on one side of the body
- Lyrics confused, difficulty understanding what you are told, or inability to speak
- Loss of vision or blurred vision in one eye
- Weakness or inability to move one side of the body
- Tremors, clumsiness, or difficulty moving
- Severe headache
- Vomiting, dizziness, difficulty with balance

Stroke: Risk factors
age
The risk increases with age after the age of 50 in men and after 60 in women.
Family history
The risk increases if, in your family:
- A close relative (father, mother, brother, sister) presented a cerebrovascular accident (CVA) before age 45
- Your father or brother presented cardiovascular disease (myocardial infarction or sudden death) before age 55
- Your mother or sister presented cardiovascular disease (myocardial infarction or sudden death) before 65.
Risk factors that you can act on
Learn to identify cardiovascular risk factors not to underestimate them.
Diabetes
One speaks of diabetes when blood sugar (blood sugar or glucose) is greater than 1.26 g / l fasting in two steps. If you have poorly controlled diabetes, excess glucose in your blood can damage the walls of your arteries.
High blood pressure
We talk about high blood pressure (hypertension) if:
- systolic blood pressure exceeds 140 mmHg or 14 cmHg
- and / or diastolic blood pressure is 90 mmHg or 9 cmHg.
- Atrial fibrillation
- Atrial fibrillation (atria of the heartbeat very fast) is a factor that can be treated.
Smoking
Tobacco promotes the narrowing of the arteries, blood clots, and the development of cardiac rhythm disorders. Smoking increases by 2 the risk of stroke.
A high cholesterol
We distinguish the bad cholesterol (LDL) cholesterol levels of good cholesterol (HDL cholesterol). If you overeat fat, if you suffer from obesity or if you do not practice physical activity, and increases bad cholesterol accumulates on the walls of your arteries as fatty deposits. Over time, these deposits can slow and block the flow of blood is atherosclerosis.
Obesity and overweight
We speak of overweight when the body mass index (BMI) greater than 25 and obese if it is greater than 30.
The presence of abdominal fat is a risk factor. There is talk of abdominal obesity when waist circumference exceeds 88 cm for women and 102 cm for men.
Physical inactivity
That is to say if you made less than 30 minutes of physical exercise a day.
- Alcohol
Alcohol, whatever its level increases the risk of hemorrhagic stroke. Consumption of more than 30 drinks per month and/or the practice of binge drinking increases the risk of ischemic stroke.

How to prevent a stroke?
- Follow the treatments for diabetes, high blood pressure, or cholesterol.
- If you are at risk, your doctor may prescribe a daily dose of aspirin to reduce the risk of forming a blood clot.
- Avoid smoking or quit smoking
- Drink alcohol in moderation
- Eat a balanced diet, do physical exercise regularly

Making good food choices, diet affects several stroke risk factors
Researchers reviewed 375 studies published between 1979 and 2004 to identify the type of power that best helps prevent stroke. According to their analysis, a low-salt diet (less than 1150 mg per day) and rich in potassium and magnesium lowers blood pressure and, thus, helps to prevent stroke. A diet containing vegetables-fruits, which are a source of antioxidant elements, gives adequate amounts of potassium. Whole grains, nuts, seeds, legumes, and dark green leafy vegetables are good sources of potassium. Studies show that people who eat about ten servings of fruits and vegetables a day, that emphasize whole grains and eat from January to February servings of fatty fish per week are less likely to suffer a stroke.
In terms of the plans, it was shown that the Mediterranean diet helps effectively prevent hypertension.
- Learn to better cope with stress
- Change contraception if necessary. Women over 35 who take a contraceptive pill and are considered at risk (because they smoke or because they have high blood pressure) should opt for another method, such as a device intrauterine or pill, which contains only progesterone.

Submit to examinations and medical treatment
- Consult your doctor at the recommended frequency by it. When a patient is at high risk of having a stroke, the doctor may listen to the stethoscope of the sound of his carotid arteries. If he suspects that artery is affected by atherosclerosis, it recommends a Doppler ultrasound of the carotid. This exam will determine the degree of narrowing of the artery.
- Regularly monitor blood pressure and if you have high blood pressure, treat, even if asymptomatic. This is the most critical risk factor to control. Healthy eating (it is important, among others, to avoid very salty food), the practice of physical exercise, moderate alcohol consumption, and the fact of quitting are some measures that help reduce the pressure of blood. Medications such as diuretics or beta-blockers may be required. View the file Hypertension for more information.
- The doctor should take blood pressure at the time of the periodic health examination. Proceed regularly to a balance of blood lipids. Take steps to correct the anomalies. See our Hypercholesterolemia sheet. In Canada, it is recommended to have routine screening every five years for men over 40 and postmenopausal or women over 50 years. People at risk (those with diabetes, hypertension, smoking, abdominal obesity, family history of cardiovascular disease, etc.) should undergo more frequent screening.
- Check your blood sugar regularly in order to prevent diabetes. In addition, although glycemic control if you have diabetes.
- At the time of the periodic medical examination, if the doctor considers it necessary, it may order a fasting glucose test.
- Consult your doctor immediately in case of abnormally fast or irregular heartbeat